Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- PWM is a simple method of using a rectangular digital waveform to control an analog variable.
- The on-off behavior changes the average power of the signal.
- Output signal alternates between ON and OFF with a specific time period.
PWM control is used in a variety of applications, ranging from communications to automatic control.It can also be used to encode information for data transmission.
How it works?
The period is normally kept constant, and the pulse width (or ON time) is varied.
Duty Cycle: It is defined as the proportion of time the pulse is ON, expressed as a percentage.
formula
Duty Cycle = (pulse ON time) / (pulse period) 100% = t ON/ T 100%
Average value of the signal = t ON*VH + (1 – t on).VL
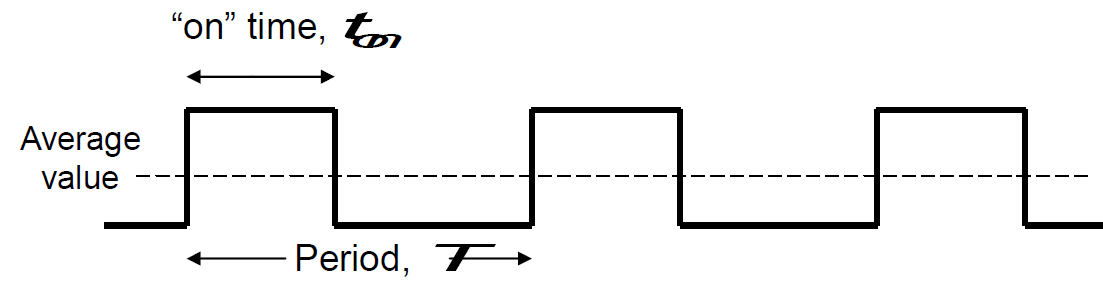
Whatever duty cycle a PWM has, there is an average value, as indicated by the dotted line.
- If the ON time is small, the average value is low; if it is large, the average value is high.
- By controlling the duty cycle, we can control the average value.
How to Extract the Average Value?
- The average value can be extracted from the PWM stream using a low-pass filter.
- If the PWM frequency and the values of R and C are appropriately chosen, Vout becomes an analog output.
- Can be used in place of a digital-to-analog converter.
Some Typical Applications
Control of DC motor: The voltage supplied to the motor is proportional to the duty cycle.Controlling the brightness of LED: The duty cycle of the voltage source determines the brightness.Control the temperature (heater): Switch ON and OFF the heater with an appropriate duty cycle.Many more…